How to support high-throughput file services with multithreading
Summary
Processing large files with many records can sometimes negatively impact system performance. In Process Commander Version 5.5, such files can be processed using multiple system threads. For example, a CSV file containing several thousand records can be processed faster if multiple records can be processed concurrently.
In this example, an insurance agent wants to import a CSV file containing several records. Each record should initiate a new policy within the system that the agent can then complete manually.
For more information about How to parse a Comma-Separated-Values file (V5.5).
Suggested Approach
The following example is an end-to-end implementation. For steps specific to multi-threaded file processing, start at Create a Service Request Processor.
To complete the example in full, complete the following steps:
- Create the Parse Delimited Rule
- Create the service activity
- Create the file service components
- Service Package
- Service Request Processor
- File Service
- File Listener
Create the Parse Delimited Rule
The Parse Delimited rule is used to indicate which properties each field of the CSV file should be mapped to. To create a new Parse Delimited rule:
- In the tool bar, navigate to Application > New > Rule > Integration-Mapping > Parse Delimited.
- Complete the New Instance of a Rule dialog. The Namespace and Record Type fields are used to define the second and third key parts of the rule.
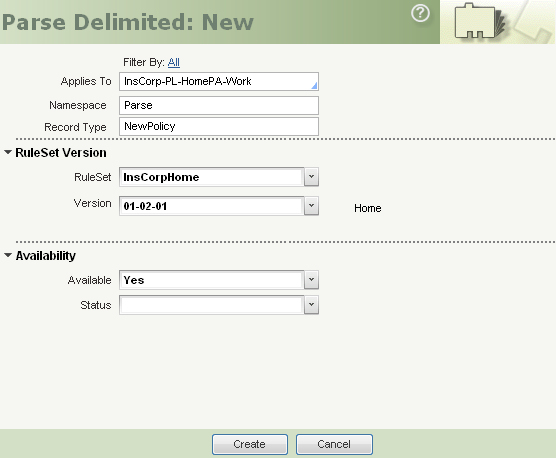
Click Create. - Complete the Parse Delimited rule form.
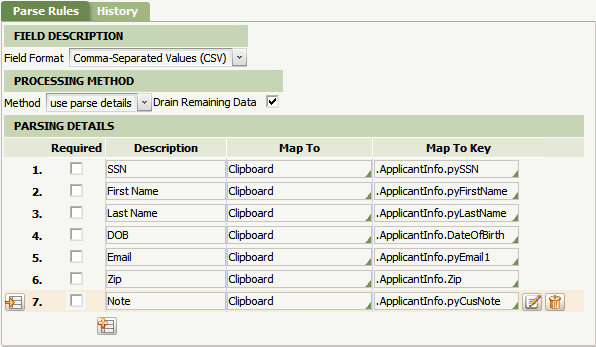
The Parsing Details area contains the fields that define which properties the contents of the CSV file are mapped to. Parsing is done from left-to-right. Each field should be listed accordingly. Save the Parse Details rule form when you are complete.
Create the Service Activity
When a file service is processing a file, it can be configured to perform an action on each record of the file, one record at a time. In addition to parsing the CSV file, the file service must also create a work object for each record.
To create the service activity:
- Define a new activity rule by using the toolbar to navigate to Application > New > Rule > Technical > Activity.
- Complete the New Rule Instance Dialog. Specify your work class as the Applies To class.
- Complete the Activity rule form.
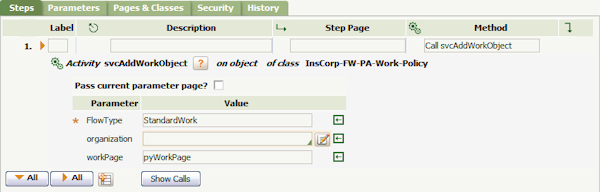
In the Method field, enter Call svcAddWorkObject to call the svcAddWorkObject function. This function creates a new work object using the Flow rule passed in the FlowType field. In this example, the FlowType is set to BatchNewPolicy, which is the Flow rule to add the created work objects to a WorkBasket specifically for new policies (NewPolicies in this example)created using this method. Set the workPage to pyWorkPage. Save the Activity rule form.
Create the File Service Components
Several components are necessary to enable Process Commander to automatically find and process a CSV file:
- A Service Package defines both the second key part of service rules and access to the service
- A Service Request Processor to queue the item
- A File Service processes the file
- A File Listener monitors a specific folder within the file system and initiates the File Service when a matching file is found
Create a Service Package
To create a new Service Package data instance:
- Locate and expand the Integration-Recources group in the Rules by Type explorer. Right-click on Service Packages and select New.
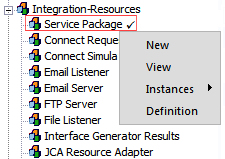
Define a Service Package Name on the New Rule Instance dialog. - On the Context tab of the Service Package form, enter your Access Group in the Service Access Group field.
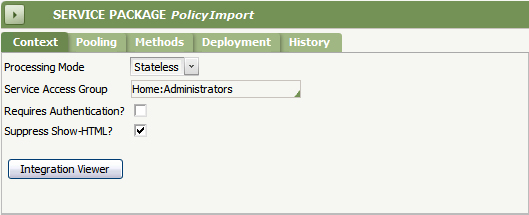
Save the Service Package form.
Create a Service Request Processor
A request processor enables asynchronous processing by defining a queue within Process Commander that can have items placed into it for processing.
To create a Request Processor:
- Using the Class Explorer, navigate to the Data-Admin-RequestProcessor-Service class.
- Click the New icon.
- Complete the New Instance of a Rule dialog. Enter the name of the Service Package you created in the previous step in the Service Package Name field. Complete the Request Processor Name field. Click Create.
- On the Queuing Options tab, enter a Queue Class Name. Use the System-Queue-ExecutionRequest-Service-Default class or define another concrete class under System-Queue-ExecutionRequest-Service-, and use it.
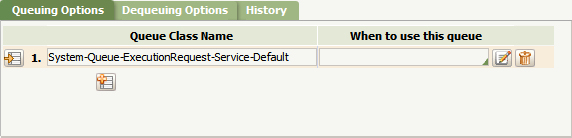
- On the Dequeuing Options tab, configure when the items should be removed from the queue.
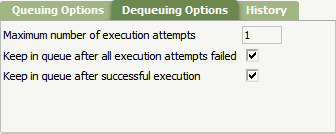
- Save the Service Request Processor.
Create the File Service Rule
To create a new File Service Rule:
- In the tool bar, navigate to Application > New > Rule > Integration-Services > File Service.
- Complete the New Rule Instance form.
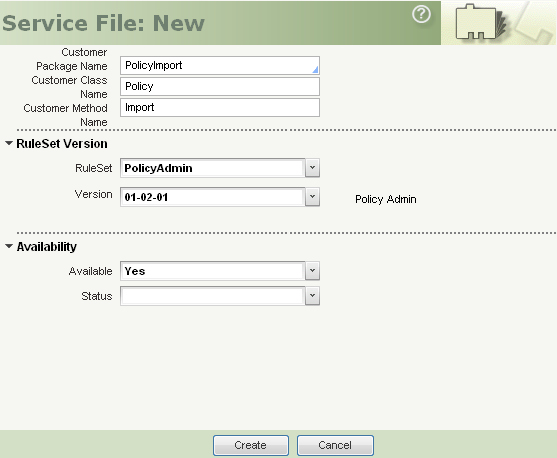
Specify the Service Package you created in the previous step in the Customer Package Name field. Complete the Customer Class Name and Customer Method Name fields to set the second and third key parts of the rule. Click Create. - Complete the Service tab by entering the work class in the Page Class field. Specify asynchronous Execution Mode and specify the Request Processor created earlier. The Requests per Queue Item field determines how many records are put into each queue item. For example, if you are importing a file with 1000 records, ten queue items will be created (1000 records ÷ 100 records per queue item = 10 queue items).
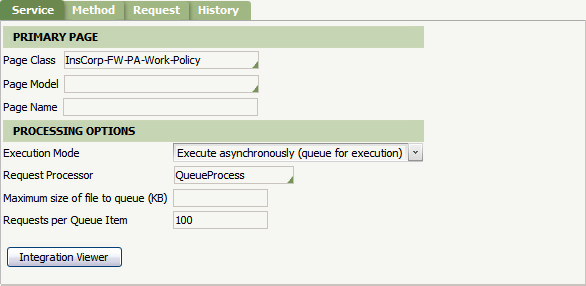
- Complete the Method tab. Specify \r\n in the Record Terminator field. Microsoft Excel inserts a carriage return and new line at the end of each record in a CSV file. Combined with the "record at a time" Processing Method, this record terminator instructs the File Service to begin processing a new record when a new line is reached.
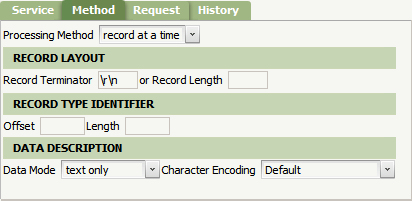
- Complete the Request tab. The Parse Segments Section defines how each record of the file is processed. To parse the fields in each record according to the Parse Delimited rule defined earlier, select Delimited ParseRule in the Map To field and Parse.NewPolicy in the Map To Key field. After each field is mapped to a property, a new work object should be created. Specify the BatchPolicyCreate activity in the Activity field. Save the File Service rule form.
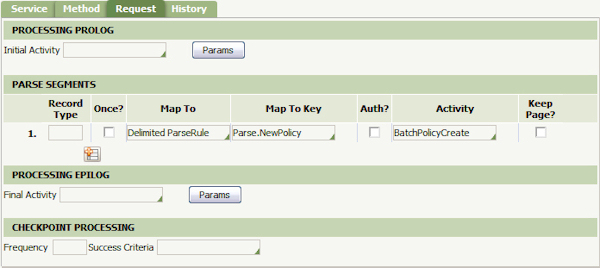
Create the File Listener
The file listener will monitor a defined folder within the file system of the server for files of a specified type. Upon locating a new file, the listener initiates a file service.
To create a new File Listener:
- In the tool bar, navigate to Application > New > Rule > Integration-Resources > File Listener. Complete the Listener Name filed and click Create.
- Complete the Properties tab of the File Listener form. Complete Source Location and Source Name Mask fields. These fields define which folder is monitored and the file type to be watched for. (Note: use the * wildcard to monitor for all files of a specific type). The Concurrent Threads field can be left with the default value. Specify the File Service rule you created by selecting the first, second, and third key parts (Service Package, Service Class, and Service Method, respectively. Save the File Listener form. Click the Test Connectivity button to ensure the Source Location exists and can be found.
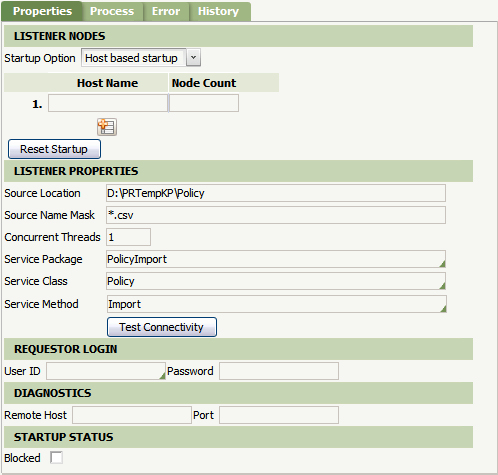
- Optional. Complete the Process tab. Change the Polling Interval to define how often the file listener checks the Source Location. (Note: Lower numbers may negatively impact performance.)
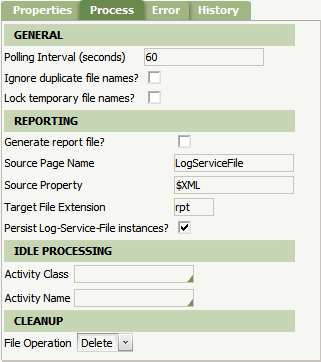
Test the System
To test this configuration, start the listener, then add a .csv file to the specified location while monitoring the file service rule with the Tracer utility. After you've seen that the file service has successfully completed, examine the contents of the NewPolicies WorkBasket.
- Start the file listener.
- Access the System Management Application by navigating to Tools > System Management Application.
- Click the Node your system is running on. In this example, the Node name is Potomac.
- Select Listener Management from the left-side navigation panel.
- Select your file listener from the Available Listeners drop down box, and click Start.
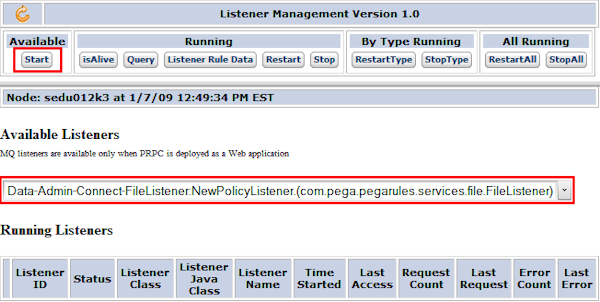
- Your listener will appear in the Running Listeners table if it has been successfully started.
- Place a .csv file in the source location.
- Using the Class Explorer, navigate to System-Queue-RequestProcessor-Service-Default. You should see items in the queue corresponding to each record in the file that was passed into the system.
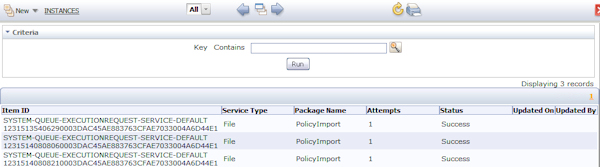
- Access the WorkManager portal and view the contents of the NewPolicies WorkBasket. These policy applications can be opened and completed by the agent.
Performance
Because of the several variables taken into account during the implementation of this feature, performance must be measured and tuned on a case-by-case basis. Parameters to consider are:
- Processing Cores — The greater the number of processing cores in your system, the greater the number of threads that are theoretically available.
- Thread Pool — The thread pool, or number of threads available to process your queue items, can have an impact on overall system performance. By default, the agent responsible for processing queue items has a thread pool of 5. To override this default setting, add the following string to the PRConfig.xml file:
<env name="agent/threadpoolsize" value="#" /> where # is equal to the number of threads in the thread pool. - Batch Size — The size of each batch determines how many batches each thread must process.
