Record the if.. then.. logic of
the decision tree in this array, which has three columns. The
unlabeled columns are known as the comparison, action, and next
value columns.
 This help topic describes the
basic format of the Decision tab.
If you encounter a Decision tab
that contains Evaluate Parameter or
Evaluate propertyname, see
Completing the Decision tab
(Advanced format).
This help topic describes the
basic format of the Decision tab.
If you encounter a Decision tab
that contains Evaluate Parameter or
Evaluate propertyname, see
Completing the Decision tab
(Advanced format).
At runtime, the system evaluates the if
portion of the array, starting at the top row, and continues as
described here until it reaches a Return
statement. If the system processes all rows but does not reach
a Return statement, it returns the
Otherwise value.
 If the Redirect this
Rule? box on the Results
tab is selected, this circumstance-qualified rule is redirected and
this tab appears blank.
If the Redirect this
Rule? box on the Results
tab is selected, this circumstance-qualified rule is redirected and
this tab appears blank.
Understanding the rows
 Each text box may
contain a value, a comparison operation for two values,
followed by an outcome. The comparison may be between two
properties or between a property and a constant value.
Each text box may
contain a value, a comparison operation for two values,
followed by an outcome. The comparison may be between two
properties or between a property and a constant value.
Click a field to make controls for that row or field
visible:
- Click Collapse All to hide subtree structures, or a
minus sign to hide subtree structures.
- Click Expand All to show all subtree structures, or
a plus sign to display specific subtrees.
- Click the pencil icon (
 ) to review a property rule (for
a field that contains a property reference).
) to review a property rule (for
a field that contains a property reference).
- Select a row and then click the
 ,
,  , or
, or  icons to insert, append, or delete a
row. (Equivalently, use the Insert ,
Shift + Insert ,
and Delete
keys).
icons to insert, append, or delete a
row. (Equivalently, use the Insert ,
Shift + Insert ,
and Delete
keys).
Field
|
Description
|
|
if / if value is
|

 Enter a
comparison using one of the six comparison
operators <, >, =, !=, >= or <=. Enter a
comparison using one of the six comparison
operators <, >, =, !=, >= or <=.
The value may be a constant or a Single
Value property reference.
This field is not visible if the action field is set
to Otherwise.
|
|
(action)
|
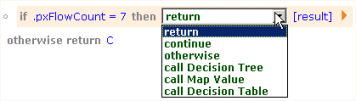
Select an action from the selection list. The action
you choose determines which branch of this decision tree
the system follows at runtime when the condition to its
left is reached and evaluates to true. Select a
keyword:
Keyword
|
Effect
|
Return
|
Causes this branch of the decision tree to end
processing when reached. If the system finds a
Return row to be true, the value in
the right column of this row becomes the result of
the decision tree evaluation.
|
Continue
|
Causes the next row of the decision tree
to be nested within this branch, The system
reflects the nesting by indenting the next row on
the form display and changing the  arrow to arrow to  to point down to that
indented row. The context for the continue
statement is the same as for the current
statement. to point down to that
indented row. The context for the continue
statement is the same as for the current
statement.
|
Call Decision Tree
|
Causes the system to evaluate another decision
tree rule, identified in the next field.
 This
choice may not be present in all cases, depending
on settings on the Results tab. This
choice may not be present in all cases, depending
on settings on the Results tab.
If, at runtime, this decision table evaluates in
a backward-chaining context (the
AllowMissingProperties parameter
to the method is true), the system evaluates the
called decision tree rule in the same way.
|
Call Map Value
|
Causes the system to evaluate a map value rule,
identified in the next field.
 This
choice may not be present in all cases, depending
on settings on the Results tab. This
choice may not be present in all cases, depending
on settings on the Results tab.
If, at runtime, this decision table evaluates in
a backward-chaining context (the
AllowMissingProperties parameter
to the method is true), the system evaluates the
called map value rule in the same way.
|
Call Decision Table
|
Causes the system to evaluate a decision table
rule, identified in the next field.
 This choice may not be present in all cases,
depending on settings on the Results tab. This choice may not be present in all cases,
depending on settings on the Results tab.
If, at runtime, this decision table evaluates in
a backward-chaining context (the
AllowMissingProperties parameter
to the method is true), the system evaluates the
called decision table rule in the same way.
|
Otherwise
|
Select Otherwise only as the
bottom, final choice in a set of alternatives,
marking the final choice. The value in the right
column of this row becomes the result of this
decision tree evaluation.
|
|
|

(next value)
|
Identify a target based on the action value.
 If
you selected If
you selected Return as the action and the
Results tab is not blank,
select one of the values listed on the Results tab.
Otherwise, enter a value or expression here that
allows evaluation of the decision tree to continue.
You can reference a property on any
page, but be sure to enter any page you reference on the
Pages & Classes tab.
Enter a value that depends on the action value
keyword:
Return or Otherwise
— Enter an expression for the result of this
decision tree when this row is the final one
evaluated.Call Decision Tree — Select
another decision tree rule. The result of that rule
becomes the result of this rule. (This choice may not
be present in all cases, depending on settings on the
Results tab.)Call Map Value — Select a map
value rule. The result of that rule becomes the result
of this rule. (This choice may not be present in all
cases, depending on settings on the Results tab.) Call Decision Table — Select a
decision table rule. The result of that rule becomes
the result of this rule. (This choice may not be
present in all cases, depending on settings on the
Results tab.)
This input field does not appear when the action value
is Continue.
Click the pencil icon ( ) to open a referenced decision tree,
map value, or decision table rule. ) to open a referenced decision tree,
map value, or decision table rule.
|
|
 Click to access an optional array of
properties and values. Click Click to access an optional array of
properties and values. Click to hide this array. (This choice may not be
present in all cases, depending on settings on the
Results tab.) to hide this array. (This choice may not be
present in all cases, depending on settings on the
Results tab.)
When the decision tree rule evaluates and this row is
the source of the results, the system also recomputes the
value of the target properties identified in this array.
Order is significant.
|
| Property
|
 Optional. Identify a
property reference to be set. Optional. Identify a
property reference to be set. |
| Value
|
Enter a value for that
property. |
| Otherwise
|
|
| Return
|
Optional. Enter an expression defining a value to
return when the decision tree evaluation does not return
another value. When the Allowed Results
list on the Results tab is
not blank, this field is required and limited to one of
the constant values listed on that tab.
If this field is blank and no other return value is
computed, the system returns the null value.
|
 About Decision Tree rules
About Decision Tree rules
![]() This help topic describes the
basic format of the Decision tab.
If you encounter a Decision tab
that contains Evaluate Parameter or
Evaluate propertyname, see
Completing the Decision tab
(Advanced format).
This help topic describes the
basic format of the Decision tab.
If you encounter a Decision tab
that contains Evaluate Parameter or
Evaluate propertyname, see
Completing the Decision tab
(Advanced format).![]() If the Redirect this
Rule? box on the Results
tab is selected, this circumstance-qualified rule is redirected and
this tab appears blank.
If the Redirect this
Rule? box on the Results
tab is selected, this circumstance-qualified rule is redirected and
this tab appears blank.![]() Each text box may
contain a value, a comparison operation for two values,
followed by an outcome. The comparison may be between two
properties or between a property and a constant value.
Each text box may
contain a value, a comparison operation for two values,
followed by an outcome. The comparison may be between two
properties or between a property and a constant value. ) to review a property rule (for
a field that contains a property reference).
) to review a property rule (for
a field that contains a property reference).