 In contrast to the persistent instances of rules and other objects in the PegaRULES database, instances on a user clipboard are temporary. When a user logs off, the system deletes the user's clipboard.
In contrast to the persistent instances of rules and other objects in the PegaRULES database, instances on a user clipboard are temporary. When a user logs off, the system deletes the user's clipboard.The rules, transactions, and other data supporting a Pega 7 Platform system are stored in one or more Oracle, IBM DB2, or Microsoft SQL Server databases. (Consult the Platform Support Guide for a current list of supported vendors and products.)
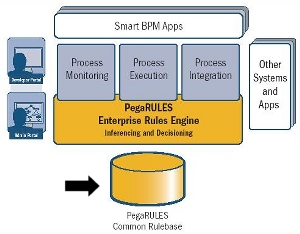
The database that contains the rules—all the instances of concrete classes derived from the Rule- base class—is known as the PegaRULES database. This database is also sometimes identified as the rulebase, but it contains more than rules.
Classes that are mapped to the PegaRULES database are known as internal classes. Concrete classes that correspond to rows of an external database are known as external classes.
 In contrast to the persistent instances of rules and other objects in the PegaRULES database, instances on a user clipboard are temporary. When a user logs off, the system deletes the user's clipboard.
In contrast to the persistent instances of rules and other objects in the PegaRULES database, instances on a user clipboard are temporary. When a user logs off, the system deletes the user's clipboard.
If the system saves an instance from the clipboard into the PegaRULES database, the saved copy remains after the user who created it logs off, and is available to other users. Thus, the PegaRULES database contains persistent objects.
Through the database table and database data instances, application developers working with database administrators determine which classes of objects are stored into which database tables.
The PegaRULES database is sometimes called a rulebase, which is a physical collection of rules and other objects in a relational database. A rulebase is different from the Rule- base class, an abstract class that has no instances.