Running PegaUnit test cases and test suites with the Execute Tests service in Pega 7.3
When you build an application on Pega Platform™ in a continuous delivery pipeline, you can use the Execute Tests service (REST API) to validate the quality of the build by running Pega unit test cases of that application.
A continuous integration (CI) tool, such as Jenkins, calls the service, which runs all the Pega unit test cases or a test suite in your application and returns the results in xUnit format. The continuous integration tool can interpret the results and, if the tests are not successful, you can correct errors before you deploy your application.
The service comprises the following information:
- Service name: PegaUnit Rule-Test-Unit-Case pzExecuteTests
- Service package: PegaUnit
- End point: http://<yourapplicationURL>/prweb/PRRestService/PegaUnit/Rule-Test-Unit-Case/pzExecuteTests
Pega Platform does not provide a test case quarantine process for this service. Test case quarantines allow you to stop non-critical tests from running if they are causing failures so that the service can continue to run.
Request parameters
The Execute Tests service takes the following request parameters, which are strings:
- Access Group – The access group associated with the application for which you want to run Pega unit test cases. This parameter is optional for Pega unit test cases and does not apply to Pega unit test suites.
- If you pass this parameter, the service runs all the test cases in the application that is associated with this access group.
- If you do not pass this parameter, the service runs all the test cases in the application that is associated with the default access group that is configured for your operator.
- TestSuiteID – The pxInsName of the test suite that you want to run. You can find this value in the XML document that comprises the test suite by clicking Actions > XML in the Edit Test Suite form. You can run only one test suite at a time. When you use this parameter, all the test cases in the test suite are run, but no other test cases in your application are run. This parameter is required for Pega unit test suites.
- If there are test suites that share the same name among applications:
- If you pass the Access Group parameter with the TestSuiteID parameter, the service runs the test suite in the application that you specified.
- If you do not pass the Access Group parameter with the TestSuiteID parameter, the system runs the test suite in the application that is associated with the default access group.
- If there are test suites that share the same name among applications:
- LocationOfResults – The location where the service stores the XML file that contains the test results. This parameter is optional for test cases and test suites.
Response
The service returns the test results in an XML file in xUnit format and stores them in the location that you specified in the LocationOfResults request parameter. The output is similar to the following example:
<test-case errors="2" failures="0" label="Purchase order transformation with a bad element in the output expected" name="report-bad-element-name" skip="0" tests="7"> <nodes expected="/" result="/">
<nodes xmlns:purchase="urn:acme-purchase-order" expected="/purchase:order[1]" result="/purchase-order[1]">
<error type="Local name comparison">Expected "order" but was "purchase-order"</error>
<error type="Namespace URI comparison">Expected "urn:acme-purchase-order" but was ""</error>
</nodes>
</nodes>
<sysout>This text is captured by the report</sysout>
<syserr/>
</test-case>
Configuring your default access group
When you run the Execute Tests service, you can specify the access group that is associated with the application for which you want to run Pega unit test cases or test suites. If you do not specify an access group, the service runs the Pega unit test cases or test suites for the default access group that is configured for your Pega Platform operator ID. To configure a default access group, complete the following steps:
- In Designer Studio, click the menu, and then click Operator.
- In the Application Access section, select your default access group.
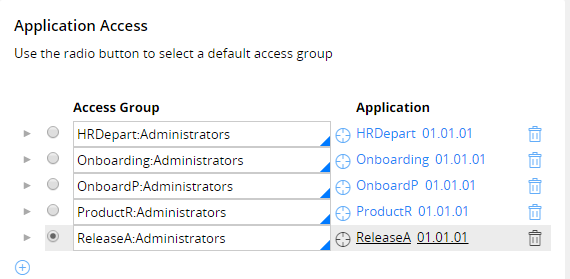 Selecting default access group configuration
Selecting default access group configuration - Click .
Configuring your build environment
Configure your build environment so that it can call the Execute Tests service and run all the Pega unit test cases or a test suite in your application. Your configuration depends on the external validation engine that you use. For example, the following procedure describes how to configure the Jenkins server to call the service.
- Open a web browser and navigate to the location of the Jenkins server.
- Install the HTTP request plug-in for Jenkins to call the service.
- Click .
- Click .
- On the Available tab, select the HTTP Request Plugin check box.
- Specify whether to install the plug-in without restarting Jenkins or download the plug-in and install it after restarting Jenkins.
- Click .
- Click .
- In the section, in the Jenkins URL field, enter the URL of the Jenkins server.
- In the section, create a record for authentication by completing the following steps:
- Click next to .
- In the Key Name field, enter a name for the authentication record.
- In the Username field, enter the operator ID that is used for authenticating the service. This operator should belong to the access group that is associated with the application that has the Pega unit test cases or test suites that you want to run.
- Select POST from the HTTP default mode list.
- Click , and then click Save.
- Add a build step to be run after the project is built by completing one of the following actions:
- Create a project if you have not already done so.
- Open an existing project.
- Click .
- In the Build section, click Add build step and select HTTP Request from the list.
- In the HTTP Request section, in the URL field, enter the endpoint of the service. Use one of the following formats:
- http://<your application URL>/prweb/PRRestService/PegaUnit/Rule-Test-Unit-Case/pzExecuteTests
- http://<your application URL/prweb/PRRestService/PegaUnit/Rule-Test-Unit-Case/pzExecuteTests?AccessGroup=<access_group_name:access_group_user>
- http://<your application URL>/prweb/PRRestService/PegaUnit/Rule-Test-Unit-Case/pzExecuteTests?TestSuiteID=<pxInsName>
If you are using multiple parameters, separate them with the & character, for example, http://<your application URL>/prweb/PRRestService/PegaUnit/Rule-Test-Unit-Case/pzExecuteTests?AccessGroup=<access_group_name:access_group_>&TestSuiteID=<pxInsName>
- From the HTTP mode list, select POST.
- Click .
- In the Output response to file field, enter the name of the XML file where Jenkins stores the output that it receives from the service. This field corresponds to the LocationOfResults request parameter.
- From the Authenticate list, select the name of the authentication record that you provided in step 6b.
- In the Post-build Actions section, select Publish Junit test result report and enter **/*.xml in the Test Report XML field. This setting configures the results in xUnit format, which provides information about test results, such as a graph of test results trends, on your project page in Jenkins.
- Click .
Running tests and verifying results
After you configure your validation engine, run the service and verify the test results. For example, in Jenkins, complete the following steps:
- Open the project and click Build Now.
- If you are running Pega unit test cases and did not specify an access group, all the test cases are run for the application that is associated with the default access group for your operator ID.
- If you are running Pega unit test cases and specified an access group, the Pega unit test cases are run for the application that is associated with the access group.
- In the Build History pane, click the build that was run.
- On the next page, click Test Result.
- Click root in the All Tests section. The results of all failed tests and all tests are displayed.
- You can expand a test result in the All Failed Tests section to view details about why the test was not successful.
Test failures
Tests are not successful in the following scenarios:
- The operator does not have access to the location of the results.
- The access group that is passed by the service either does not exist or no access group is associated with the operator ID.
- An application is not associated with the access group passed by the service.
- No Pega unit test cases or test suites are in the application.
