|
|
Most activities referenced in a flow are defined in the
Work- base class, or a class derived from the Work- base class.
To become a Notify, Integrator,
Utility, Routing, or
Assignment activity, they must meet other
constraints and have this type recorded in the Activity
Type field of the Security
tab.
Click the Preview button in the toolbar (![]() ) or type the equivalent keyboard shortcut
) or type the equivalent keyboard shortcut
CTRL+ALT+P to see a step-by-step verbalization or
English text description of this activity (informally known as
the "Describe This Rule" presentation). The system
creates an HTML topic describing each step of the activity,
with links to other rules referenced by the step.
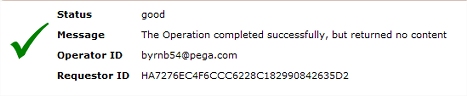
When a top-level activity completes but produces no HTML display, by default a "No content" form appears with a green checkmark:
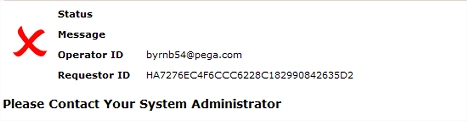
When an activity fails or encounters an uncaught exception, by default a "Please contact your system administrator" window appears with a red X mark:
Your application can override and localize standard harness rules that present these two windows, and can override the standard activities that call the harness rules. See See How to customize the activity success and exception windows.
![]() The standard function
callActivity() in the Pega-RULES
Utilities library calls an activity, but returns
only void, not a value result. You can execute an activity in
an expression, but only for its side effects. Identify the primary page, the activity, and the
parameter page. For example:
The standard function
callActivity() in the Pega-RULES
Utilities library calls an activity, but returns
only void, not a value result. You can execute an activity in
an expression, but only for its side effects. Identify the primary page, the activity, and the
parameter page. For example:
@Pega-RULES:Utilities.callActivity(pyWorkPage,
MyActivity,
tools.getParameterPage());
When you save an activity rule, the system converts the steps to Java source code. As a learning or debugging aid, you can review this Java code.
Click the Show Java toolbar button
(![]() ) to see the system-generated Java code that
implements the activity. The window presents a read-only
preview of the Java that implements this rule instance. This
Java code is not identical to the Java that is executed at
runtime, which includes Java code inlined from other rule
instances and reflects rules in the requestor's RuleSet
list.
) to see the system-generated Java code that
implements the activity. The window presents a read-only
preview of the Java that implements this rule instance. This
Java code is not identical to the Java that is executed at
runtime, which includes Java code inlined from other rule
instances and reflects rules in the requestor's RuleSet
list.