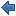
 Grid layout - General tab
Grid layout - General tab

|

|
Click the magnifying glass  in the Grid Repeat Layout header to display the Properties panel, and then select the General tab to define the source of the grid.
in the Grid Repeat Layout header to display the Properties panel, and then select the General tab to define the source of the grid.
| Data Source | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source |
Select either a If you select |
||||||||||||
| List/Group | If you specified Property, select the Page List or Page Group property that you want to use as the data Source. You can reference nested Page Lists and Page Groups; for example, Page.Page.Page.Page.PageList; or DataObject.PageList. |
||||||||||||
| Applies To | If you specified Report Definition, select the Applies To key part of the rule. |
||||||||||||
| Report definition |
If you specified If the report definition has parameters, you can pass parameter values to the report definition. Press the down arrow in the Value field to specify the value that you want to pass to the report definition. Using parameters, you can filter the results that are returned to the grid from the report definition. See About Report Definitions. |
||||||||||||
| Create grid dynamically |
Select this checkbox to create a dynamic column in the grid, sourced from the Report Definition. At runtime, the grid generates the columns contained in the specified Report Definition. The grid columns display as they are defined in the Report Definition; for example, the column name, heading, width, format values, and show/hide settings, display as defined in the Report Definition source. The runtime display automatically updates when the Report Definition changes; there is no need to update the section containing the grid. A dynamic column is added in the section at design time. You can add static columns before or after the dynamic column in the grid. If you want to specify a virtual Report Definition page, a clipboard page of type |
||||||||||||
| Specify virtual report definition |
Displays when the Source of the grid is a This advanced option enables you to specify the name of a clipboard page of type RULE-OBJ-REPORT-DEFINITION. When specified, the grid uses the report definition specification in this clipboard page, rather than the one specified in the Report definition bound as the grid source. Using this technique, you can display columns that are hidden in the report definition, hide columns that are visible, and make subtle changes to the presentation. See About Report Definitions. |
||||||||||||
| Data Page |
If you specified If the data page has parameters, you can pass parameter values to the data page. In the Value field, specify the value that you want to pass to the data page. Using parameters, you can filter the results that are returned to the grid from the data page. When a grid is bound to a data page that accepts parameters and the parameter value uses a property reference, the grid automatically refreshes with new items whenever the property value changes. No additional configuration is required. If you do not want the page to refresh automatically with new items whenever the property value changes, select the Disable automatic refresh checkbox. |
||||||||||||
| Specify custom results page |
Appears if you specified Select this checkbox if you want to specify a custom results page. In the field that displays, specify the existing clipboard page to which you want to save the results. |
||||||||||||
| Grid Summary | Type a description of the grid for accessibility purposes. This description does not display in the UI. It is stored in the HTML and accessed by screen readers. | ||||||||||||
| Pagination | |||||||||||||
| Pagination format |
Optional. If the data results comprise more than a single page (approximately 20 rows of data), you may want to specify a paging format: Progressive paging: Limits the number of rows initially loaded to render the page more quickly. Remaining items are loaded as-needed, as the user scrolls through the list. When a user drags the scrollbar and releases, all rows above that point in the grid are loaded. Unlike traditional paging, in which users can access specific pages of data using paging controls, progressive paging enables users to access the entire data set by scrolling. Users can act on the full data set, dragging and dropping to re-order the list and sorting and filtering the entire list. For a description of a working example, see PDN article When and how to use progressive paging to load data into grids. Progressive paging is available for all data sources, including report definition, and can be used with grids. Progressive paging is not available for tree or tree grids. Traditional paging: Retrieves a segment, known as a page, from the total data set on the clipboard. You can specify the number of rows per page and select a page navigation control format. The paginate gadget (pyGridPaginator section) is automatically added to the right-most cell in Action Top. You can drag and drop the gadget onto any cell in an action area (do not drop into the repeating area). Users can access data via the paging controls and can drag and drop rows within a page. The options are:
|
||||||||||||
| Size grid height to content | Appears if you select Progressive as the Pagination format. Select to enable the height of the grid to automatically adjust, eliminating unnecessary white space. For example, if fewer results are returned than the number specified in Page size (number of rows), the grid height automatically adjusts. | ||||||||||||
| Page size (number of rows) | Appears if you select a Pagination format other than None. Select the items rows per page (20 is the default). To specify a custom value, select Other and enter a positive integer in the empty field. |
||||||||||||
| Specify pagination activity | Appears if you selected a paging option in the Pagination format field. Select if you want to specify a pagination activity. | ||||||||||||
| Pagination activity |
Select a custom activity that populates the clipboard from a Page List in a page size you define. Because the activity limits clipboard size, this option is useful when retrieving large amounts of data from an external Web service or database. You can also use this activity to control sorting and filtering behavior. Click the magnifying the glass icon For guidance on configuring the parameters in your activity, use a copy of the standard template activity pyTemplateAdvancedGridActivity. |
||||||||||||
| Pagination activity manages sorting |
Appears if you select the Specify pagination activity checkbox and specify a Pagination activity. Select this checkbox if you want the activity to control sorting behavior. See standard template activity for parameters. If you do not select this option, the Obj-Sort method is applied to the page in view mode only. |
||||||||||||
| Pagination activity manages filtering |
Appears if you select the Specify pagination activity checkbox and specify a Pagination activity. Select if you want the activity to control filtering behavior. See standard template activity for parameters. |
||||||||||||
| Conditions | |||||||||||||
| Grid visibility |
Select one of the following to control when the grid is visible:
|
||||||||||||
| Row visibility |
Select one of the following to control when grid rows are visible:
|
||||||||||||
| Row Refresh |
Select one of the following to control when grid rows refresh:
|
||||||||||||
| Run visibility condition on client? |
Appears when you specify a simple expression as a Grid visibility condition. Select this checkbox to cause evaluation and execution of the condition each time the value of a property stated in the condition changes. If unselected, the expression is evaluated and the condition executed when the form is initially presented and whenever the form is refreshed. By default, controls that allow typing, such as Text Input, are evaluated when the user leaves the field. To re-evaluate conditions as the user types, use the Apply Conditions action with a Keyboard event. See Control Form — Completing the Control tab. |
||||||||||||
| Header and Footer | |||||||||||||
| Display grid header | Select if you want to display a grid header. You can include actions, such as add and delete row, in the grid header. If pagination is enabled in the grid, the controls for pagination display in the grid header. | ||||||||||||
|
Display header |
Appears if Display grid header is selected. Select one of the following to control when the grid header displays:
|
||||||||||||
| Display grid footer | Select if you want to display a grid footer. You can include actions, such as add and delete row, in the grid footer. | ||||||||||||
| Display footer |
Appears if Display grid footer is selected. Select one of the following to control when the grid footer displays:
|
||||||||||||

|
Harness and Section forms - Adding a grid layout
|